Any satellite communication line includes transmitter and receiver ground stations, uplink and downlink, and communication satellite transponders. It can be seen that the ground station is an important part of the satellite communication system. So what are the categories of ground stations? How do we choose? Below we will introduce the main categories of ground stations for you, please read with patience.
What Are the Classifications of Ground Stations?
The basic function of the ground station is to transmit signals to the satellites, and at the same time receive the signals retransmitted by the satellites from other ground stations. Depending on the nature and purpose of the satellite communication system, there are different forms of ground stations.
According to whether the ground station can be moved or not:
It can be divided into fixed stations, mobile stations (such as shipborne stations, airborne stations and vehicle-mounted stations, etc.), and detachable stations (ground stations that can be disassembled and transferred in a short time).
In fixed stations, it can be divided into large standard stations and small non-standard stations. The former is mostly used for international communication and communication between large domestic cities, while the latter is mostly used for domestic medium and small cities or military communication;
mobile ground stations are especially vehicle-mounted. The station, because of its maneuverability and flexibility, has a wide range of applications in military communications.
Classified by G/T value:
Ground station performance index G/T value is an important technical performance index reflecting the ground station receiving system. where G is the receiving antenna gain, and T is the equivalent noise temperature representing the noise performance of the receiving system. The larger the G/T value, the better the performance of the ground station receiving system.
Classification by Use:
It can be divided into civil, military, broadcasting, navigation, experimental and other ground stations.
Classification by Antenna Diameter:
It can be divided into 1-meter station, 5-meter station, 10-meter station, 30-meter station and so on.
Classification According to the Characteristics of the Transmitted Signal:
Can be divided into analog communication station and digital communication station.
How to Choose a Ground Station and What Are the Requirements?
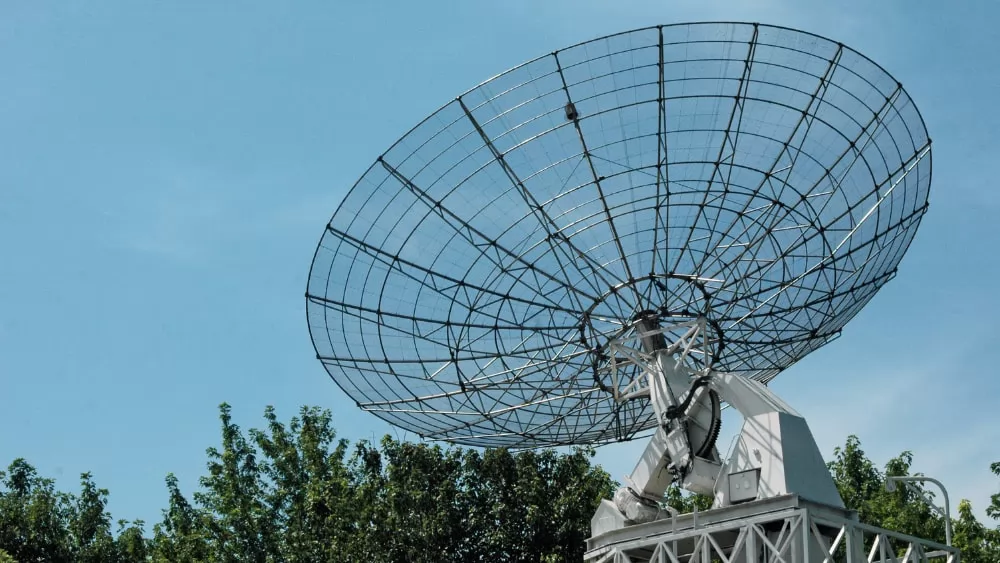

1. Operating frequency range
This refers to the RF operating range of the ground station. For example, a satellite ground station operating at 6/4GHz, in the FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) system, should be within the uplink frequency range of 5.925 to 6.425GHz, and one or several frequencies should be selected as the local station's frequency according to the allocation of the system.
Uplink transmission frequency; and in the upper ground frequency range of 3.700 ~ 4.200, according to communication needs, receive one or several radio frequency signals forwarded by the satellite. In addition, the replacement of the carrier frequency if necessary should also be considered. The ground station used for TDMA (time division multiple access) only needs to meet the frequency band requirements of the communication channel (depending on the signal transmission rate of the system) because the radio frequency of all stations is the same.
2. Performance index G/T value
When the power of the satellite transponder cannot be increased arbitrarily due to the limitation of various factors, the requirements for the G/T value of the ground station are relatively high. To this end, on the one hand, the ground antenna must have a sufficiently large gain G, and on the other hand, the noise introduced by the entire receiving system (usually represented by the noise temperature T of the system) should be as small as possible. The G/T value represents the performance of the receiving ground station, so it is called the ground station performance index.
3. Effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) and its stability
The product of the gain of the ground station antenna and the input power is called the effective isotropic radiated power. Its meaning is: in order to keep the receiving level of the same receiving point unchanged, the equivalent power that should be fed in when the original directional antenna is replaced by a non-directional antenna. EIRP is an important indicator to characterize the launch capability of the ground station.
The larger the value of this index, the stronger the launch capability of the ground station. For the ground station, its transmit power is also required to be very stable, that is, the EIRP cannot have a large change, otherwise the communication quality of the system will be affected. This requires no more than +/-0.5dB variation in the EIRP rating.
4. Diffusion of radio frequency energy
When transmitting telephone signals, the radio frequency energy at light load is required not to exceed the specified value to reduce the interference of intermodulation noise.
5. Interference wave radiation
The interference wave generated by the ground station will cause interference to other ground stations and the ground microwave communication system. Therefore, the intermodulation component caused by multi-carrier operation should be close to 2dBW/4KHz, and the total out-of-band radiation should be less than 4dBW/4KHz.
Introduction to the Composition of the Ground Station

The ground stations used in various satellite communication systems are diverse, and a typical duplex ground station equipment should include a channel termination subsystem, a high-power transmitting subsystem, a high-sensitivity receiving subsystem, and an antenna feeding subsystem. Servo tracking sub-system, power sub-system and monitoring sub-system and other parts.
1. Channel terminal subsystem
The role of the originating device in the channel terminal subsystem is to process the baseband signal and modulate the intermediate frequency (such as 70MHz); the role of the receiving device is the opposite of the above process.
Channel terminal equipment can be divided into analog channel terminal equipment and digital channel terminal equipment according to the difference in signal processing; according to communication services, it can be divided into TV, telephone, data and other channel terminal equipment.
The functions of each unit are as follows: The function of the telephone baseband processing unit is to process the frequency division multiplexed baseband signal sent by the sending terminal, that is, to perform pre-emphasis, automatic gain control, peak amplitude limiting, adding energy diffusion signals and adding pilot signals, etc. The function of the frequency modulator unit is to use the signal output from the baseband processing unit to 70MHz intermediate frequency FM signal; the function of the intermediate frequency amplifier unit is to amplify the intermediate frequency FM signal, and to balance the amplitude-frequency characteristics and group delay characteristics to a certain extent.
2. Launch subsystem
In a standard ground station, it is necessary to transmit a high-power microwave signal of several hundred watts or even a dozen kilowatts to the satellite. To achieve multiple access communications, several carriers are often transmitted simultaneously to other ground stations. Therefore, the ground station should be able to work under the condition of high voltage, high power, wide frequency band and multi-carrier. This system includes up-converter, automatic power controller, transmit wave synthesizer, exciter and high-power amplifier.
The IF wideband FM signal sent from the sending terminal is converted into a microwave signal by an up-converter (generally a parametric frequency converter). The local oscillation frequency used by the up-converter is generated by the local oscillator (also known as the pump source). The local oscillator generally adopts the method of phase-locking and frequency doubling of the crystal oscillator to generate the microwave oscillation frequency with high frequency stability.
Do You Need to Buy a Ground Station?
Newstar is a leader in communication ground stations in China, specializing in providing large-scale satellite ground stations to overseas customers. Our earth stations offer maximum durability with minimal maintenance. Not only that, we can also provide you with professional installation, training, maintenance and other services. Provide you with a full range of services. If you need, please contact us now. We will provide the most reasonable solution for your project.