In the modern digital era, satellites enable global connectivity, Earth observation, and scientific discovery. Yet, these orbiting assets would be useless without satellite ground stations—the critical terrestrial infrastructure that enables two-way communication with spacecraft.
This in-depth guide covers everything beginners and professionals need to know: from fundamental concepts and components to real-world applications, types, selection criteria, and up-to-date cost analysis
1. What is a Satellite Ground Station?
A satellite ground station (also called an Earth station) is a terrestrial radio facility designed for extraterrestrial communication with satellites in orbit. It serves as the vital link between the space segment (satellites) and the ground segment (terrestrial networks and end users).
Ground stations transmit commands (uplink) and receive telemetry, imagery, and data (downlink), compensating for challenges like Doppler shift, propagation delay, and extremely weak signals from thousands of kilometers away.
2. Core Functions: Why Do We Need Them?
Ground stations perform three essential roles collectively known as TT&C (Telemetry, Tracking, and Command):
- Data Downlink: Receiving high-resolution imagery, scientific data, or broadband signals in frequency bands such as S, C, X, Ku, or Ka.
- Command Uplink: Sending operational instructions, software updates, or orbit correction maneuvers.
- Tracking & Monitoring: Continuously monitoring satellite health (battery, temperature, attitude) and precisely tracking its position.
3. Key Components: The Anatomy of a Station
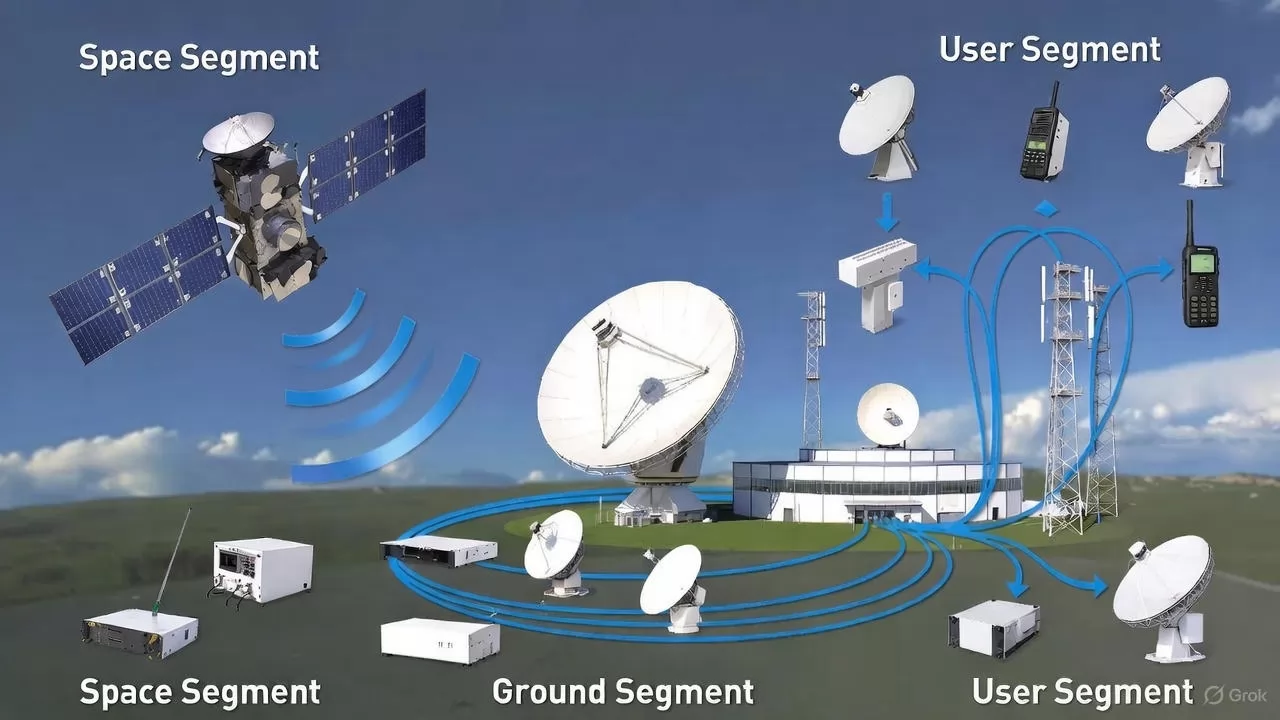
1. Space Segment
-
Spacecraft: The primary satellite or vehicle in orbit that facilitates communication by transmitting and receiving signals between the ground and user segments.
2. Ground Segment
The ground segment consists of the infrastructure required to manage the satellite and its mission:
-
Ground Station: Equipped with a large parabolic antenna, this facility serves as the direct radio link to the spacecraft in orbit.
-
Control Center: The central hub that processes data and coordinates all operations between ground stations, remote terminals, and the pre-launch facilities.
-
Remote Terminals: Computer systems that allow operators to interact with the control center from different locations.
-
Pre-launch Infrastructure: Includes the I&T Facility (Integration and Testing) and the Launch Facility, which are responsible for the spacecraft before it reaches orbit.
3. User Segment
-
Customer Terminals: The end-user equipment, such as satellite dishes or handheld radio devices, that receives the final service or data downlinked from the spacecraft.
4. Main Applications: Real-World Use Cases
- Meteorology: Receiving data from GOES, Himawari, and Fengyun satellites for weather forecasting.
- Earth Observation: Downloading imagery from Landsat, Sentinel, or commercial constellations like Maxar.
- Broadband & Backhaul: Supporting Starlink, OneWeb, and traditional geostationary services.
- Broadcasting: DTH television and radio distribution.
- Defense & Scientific Missions: NASA DSN, ESA ESTRACK for deep-space probes.
5. Types of Satellite Ground Stations
| Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Earth Stations | Large permanent installations (3–13m+ dishes) | Teleports, gateways, mission control centers |
| Flyaway Stations | Portable, case-packed systems | News gathering, disaster response |
| Drive-Away / SNG | Vehicle-mounted auto-deploy antennas | Live broadcasting, military operations |
| VSAT Terminals | Small consumer/business dishes (0.75–2.4m) | Rural internet, maritime, aviation |
6. Selection & Design Considerations
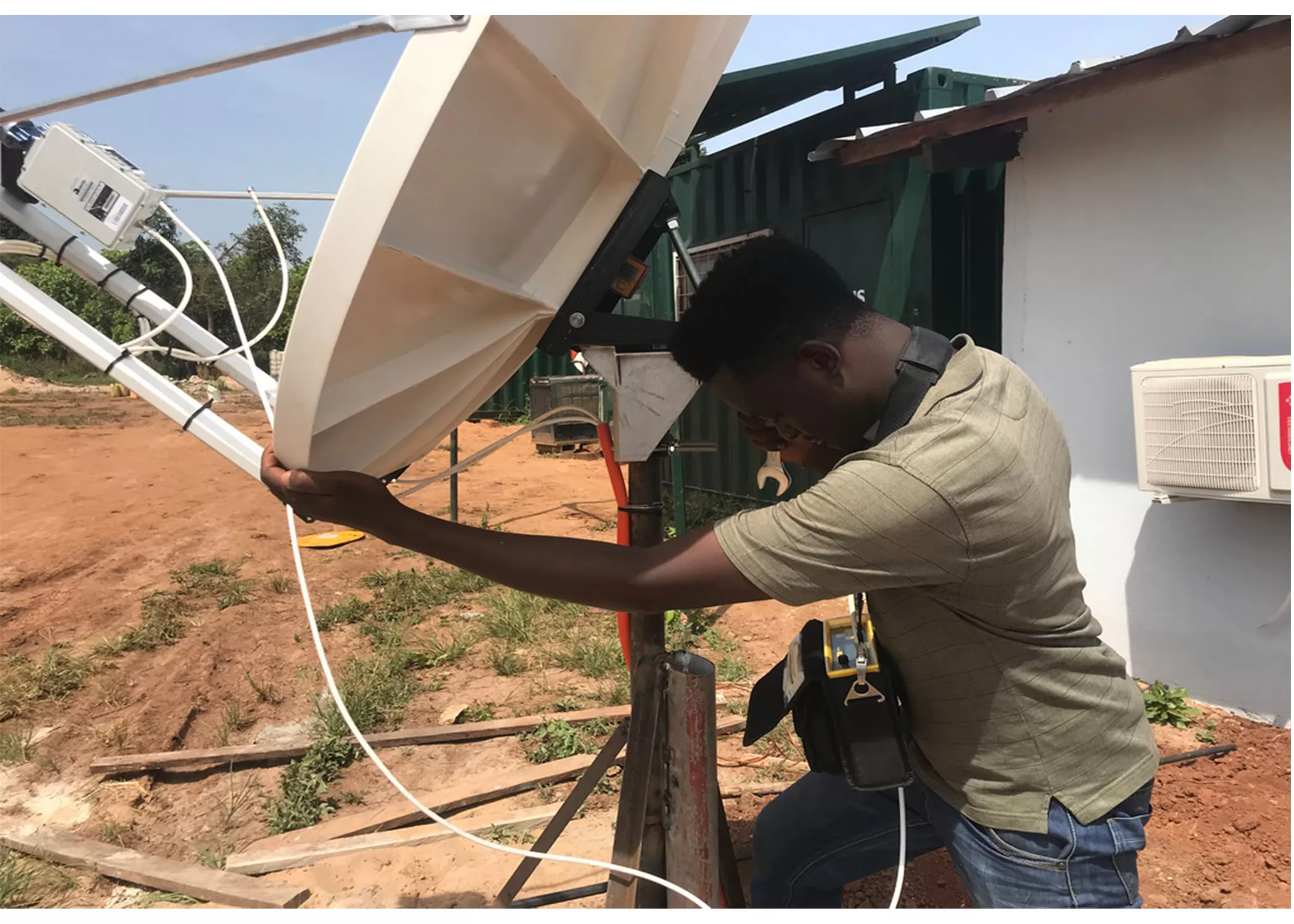

- Link Budget Calculation: Ensures sufficient margin against rain fade and noise.
- Frequency Band Selection: C-band (rain-resistant), Ku/Ka-band (high bandwidth but weather-sensitive).
- Interference Protection: Filters against 5G/terrestrial signals.
- Tracking Requirements: Fixed pointing for GEO; full-motion for LEO constellations.
- Regulatory Compliance: ITU coordination and local licensing.
7. Cost Analysis: How Much Does a Ground Station Cost?
| Component / Type | Estimated Cost (USD) | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer VSAT (0.75–1.2m) | $500 – $2,500 | Mass-produced hardware, self-install |
| Professional Flyaway (1.2–2.4m) | $15,000 – $60,000 | Carbon fiber, rugged cases |
| Fixed Earth Station (3.7–7.3m) | $50,000 – $250,000 | Foundation, motorization, redundancy |
| Gateway / Teleport Antenna (9m+) | $300,000 – $1.5M+ | High-power amplifiers, full redundancy |
8. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a ground station and a teleport?
A ground station is the antenna system itself; a teleport is a commercial facility hosting multiple ground stations connected to fiber backbones.
Does weather affect performance?
Yes—rain fade impacts Ku/Ka-band. Systems use adaptive power control and site diversity to mitigate.
How long do ground stations last?
Mechanical structures: 20–30 years. Electronics typically upgraded every 5–10 years.
Are cloud-based ground stations replacing traditional ones?
Services like AWS Ground Station and Azure Orbital are gaining traction for LEO constellations, reducing CAPEX.
At Newstar, we specialize in the engineering and manufacturing of professional-grade hardware for the Ground and User Segments. With over 10 years of experience, we provide high-performance Earth Station Antennas, Flyaway and Drive-Away solutions, and customized telemetry products designed for reliability in the most demanding environments. Whether you are building a permanent gateway or a mobile emergency network, Newstar offers the technical expertise and self-owned factory support to ensure your mission's success.
Explore our professional antenna solutions at: