Ground stations form the communication bridge between satellites and Earth. Depending on operational environment, mobility requirements, and mission objectives, different types of ground stations are used to ensure reliable satellite links. This guide explains the four main types of ground stations and how they are applied in real-world satellite systems.
What Is a Ground Station?
A ground station is a facility or system that communicates with satellites via radio frequency links. It supports satellite telemetry, tracking, command, and payload data transmission, and is an essential component of satellite communication, Earth observation, navigation, and space exploration missions.
Why Are There Different Types of Ground Stations?
- Different mission durations and operational timelines
- Varying mobility and deployment speed requirements
- Environmental and geographic constraints
- Differences in coverage, latency, and data throughput needs
Main Types of Ground Stations Explained
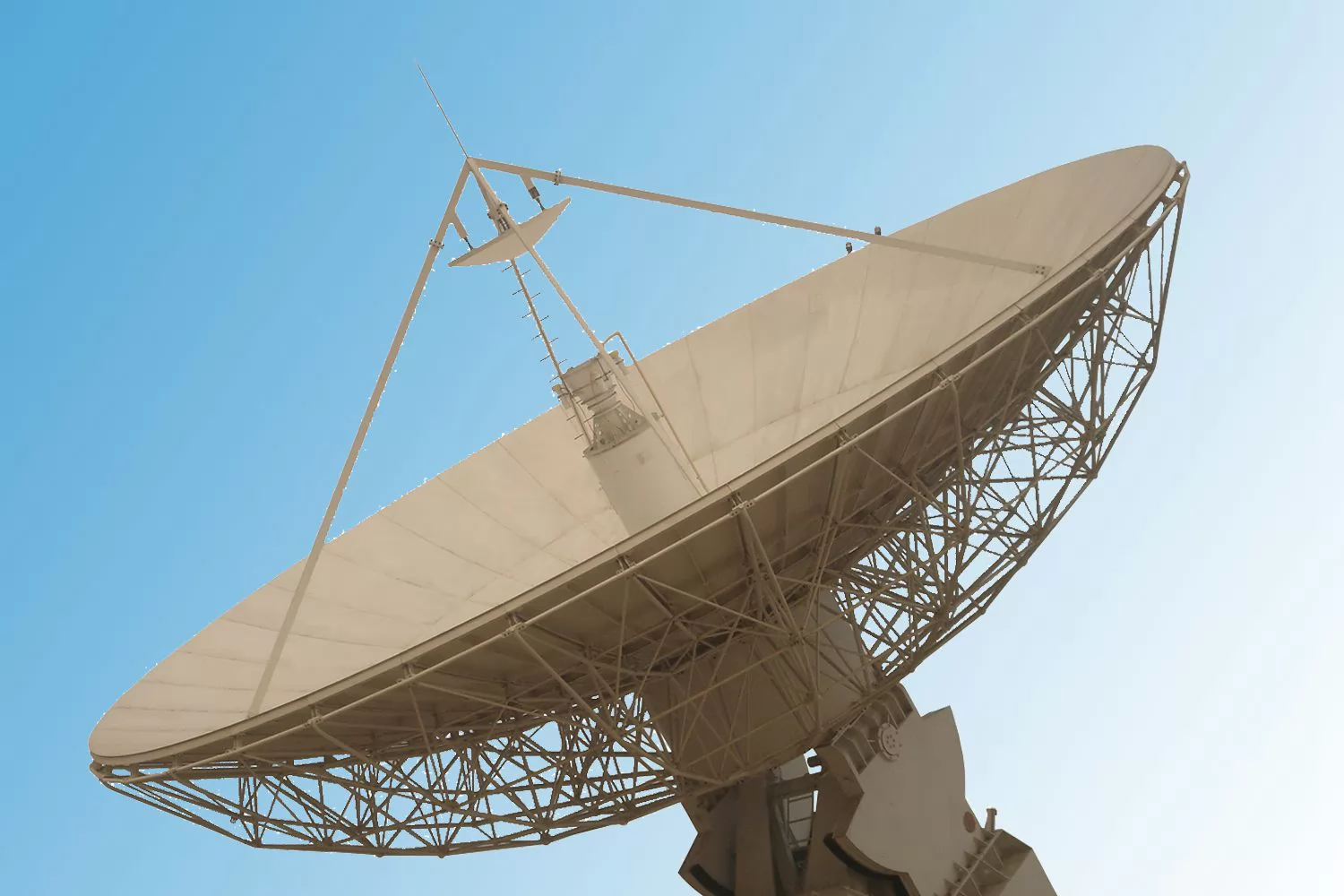
Fixed Ground Stations
Fixed ground stations are permanently installed satellite communication facilities built at carefully selected geographic locations. They are designed for long-term operation and high reliability.
Typical characteristics include:
- Large aperture antennas with stable foundations
- High transmit power and multi-band capability
- Dedicated infrastructure for continuous operation
Fixed ground stations are widely used for telemetry, tracking, and command functions, as well as high-volume data downlink in Earth observation, satellite broadcasting, and scientific missions. Their main limitation is the high initial cost and lack of deployment flexibility.

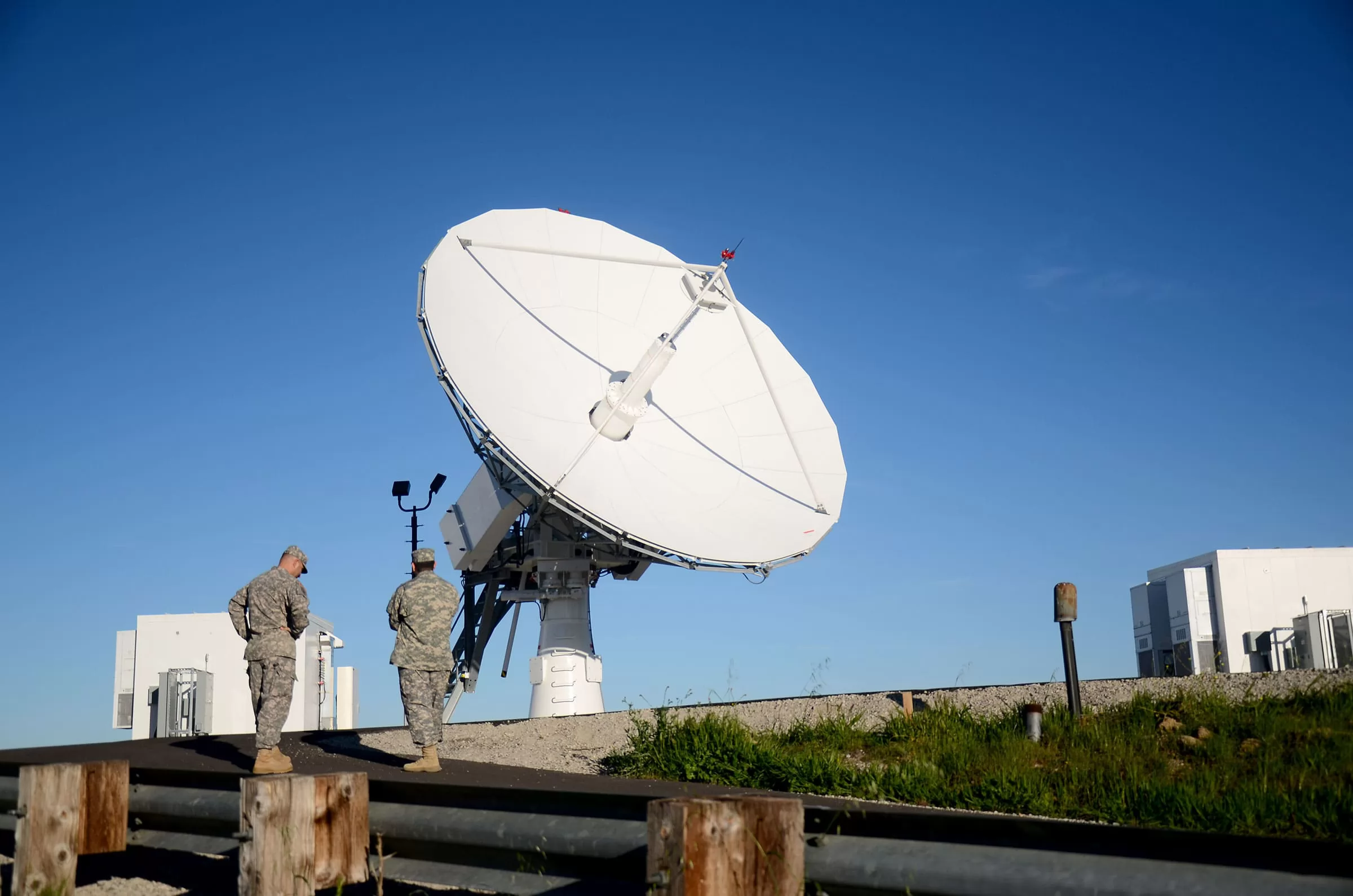
Mobile Ground Stations
Mobile ground stations are designed to be transported and deployed quickly, making them suitable for temporary or rapidly changing mission environments.
Common use cases include:
- Emergency and disaster response communications
- Military and security operations
- Temporary field testing and remote projects
While mobile ground stations offer excellent flexibility, they typically use smaller antennas and lower power systems, which can limit data throughput compared to fixed installations.

Maritime Ground Stations
Maritime ground stations are specialized systems installed on ships and offshore platforms to enable satellite communication at sea.
Key design requirements:
- Stabilized antennas to compensate for vessel motion
- Resistance to salt, humidity, and harsh weather
- Continuous tracking of satellites while underway
These systems are essential for commercial shipping, offshore energy operations, and naval communications, where terrestrial networks are unavailable.
_1766023213_WNo_910d910.webp)
Spaceborne Ground Stations (Relay Stations)
Spaceborne ground stations, also known as relay stations, operate aboard satellites to relay data between spacecraft and Earth-based ground infrastructure.
They are typically used to:
- Extend communication coverage for LEO satellites
- Increase contact time for Earth observation missions
- Support deep-space and multi-orbit architectures
Although spaceborne relay stations reduce reliance on ground infrastructure, they introduce additional system complexity and dependency on inter-satellite links.
_1766023232_WNo_918d918.webp)
Comparison of Ground Station Types
| Type | Mobility | Coverage | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | None | Regional / Global (networked) | Earth observation, broadcasting, scientific missions |
| Mobile | High | Local / Temporary | Emergency response, military, field operations |
| Maritime | High (sea-based) | Oceanic | Shipping, offshore platforms, naval operations |
| Spaceborne | Orbital | Multi-orbit / Global | Relay networks, deep space missions |
How to Choose the Right Type of Ground Station
Selecting the appropriate ground station type depends on mission objectives, required coverage, deployment speed, and budget constraints. In many satellite systems, a hybrid approach combining multiple ground station types is used to maximize coverage and operational resilience.
Future Trends in Ground Station Types
- Cloud-based and virtualized ground station networks
- Software-defined and automated ground systems
- Integration with multi-orbit satellite constellations
FAQs About Types of Ground Stations
How many types of ground stations are there?
Ground stations are commonly divided into four main types: fixed, mobile, maritime, and spaceborne.
Which type of ground station is most flexible?
Mobile ground stations offer the highest flexibility due to their rapid deployment capability.
Conclusion
Each type of ground station plays a distinct role in satellite communication systems. Understanding their differences helps operators design efficient, reliable, and mission-appropriate ground segment architectures.
NewStar is an engineering-focused provider of satellite ground station solutions, supporting fixed, mobile, maritime, and multi-orbit communication systems. The company works with satellite operators and system integrators to design, deploy, and maintain ground segment architectures tailored to mission-specific requirements, including telemetry, tracking, command, and high-throughput data transmission.